2. Cooperative specificities
s
” The purpose of a cooperative shall be to promote the economic and business interests of its members by way of the pursuit of economic activity where the members make use of the services provided by the cooperative or services that the cooperative arranges through a subsidiary or otherwise. The rules of a cooperative can regulate its purpose differently.”
Finnish Cooperative Act
1. Business and community at the same time
Cooperatives function in the market economy, as do other businesses. Cooperatives are an excellent legal form for those whose entrepreneurship is more based on cooperation than capital injections.
A cooperative has a dual nature: it is a business and a community at the same time. As a business, it aims at a high profitability, which allows it to offer benefits to its members. As an objective, profitability is not to be confused with maximizing the result, which is most often the starting point of limited companies. Compared to its pair companies, a cooperative’s financial result can be weaker due to its members’ financial benefits distributed to its members during the accounting year. This does not mean that a cooperative should be less profitable than a limited company. In a cooperative, the benefit goes to those who take part in the life of the enterprise or take advantage of its services. The members can have a customer relationship with the cooperative they own as consumers, producers, or users of services.
The incorporation of a cooperative does not necessarily involve a large injection of initial capital. A cooperative is a more secure alternative for being a one-person company and provides a safety net, too; together, you are not alone. Working together as an enterprise, we diminish the business risk and gain more ability to dare. Compared with a limited company, a cooperative is more flexible, be it for the number of its members, for instance, and more equal, because all members have the same decision making power.
2. Other cooperative specificities
Because one or more people can incorporate a cooperative, it is a well-suited legal form for a small or family company. The Finnish Cooperative Act does not limit the residence or living place of the cooperative members. In consequence, people outside EEA can be members of a cooperative. The law does not contain any rules on the minimum capital of a cooperative, either.
The members of a cooperative are not personally liable for the obligations of the cooperative. This is called the principle of limited liability, which is the same in limited companies. The situation is different for sole traders, partnerships, or limited partnerships: the entrepreneur or entrepreneurs are entirely liable for the companies’ obligations. Outgoing members of a cooperative receive (in the general rule) the amount of money they contributed for their share one year after the closing of the financial year during which they left the cooperative, provided that the cooperative has distributable profits (Finnish Cooperative Act, Section 10:1).
A cooperative is a joint enterprise owned and democratically administrated by its members. The owners decide on equal footing by applying the principle of one member one vote, not according to their proportionate holdings. This ensures a cooperative is quite difficult to take-over. A statutory rule may waive the principle of one member one vote. In the so-called primary cooperatives, the members of which are only natural persons, the number of votes of one member can be at most 20 times the number of votes of any other member. In secondary cooperatives, according to the rules of which the majority of their members are cooperatives or other corporate bodies, the principle of one member one vote can be freely waived.
The surplus of a cooperative belongs to the cooperative itself. However, its statutory rules can provide for the distribution of the surplus among its members, in which case the allocation rules must be defined as well. Even if the main objective weren’t to produce a surplus, it would be a good idea to have some money left to develop the enterprise. The cooperative’s net assets also belong to the cooperative itself, and they can only be distributed to the members at the winding-up of the cooperative.
According to the Finnish Cooperative Act, a cooperative can be ideological and not-for-profit. Its purpose can be defined as “the fostering of the cooperative ideal” or another common good purpose in its statutory rules. Therefore, an association of different cooperatives or a village organization could work as a cooperative and exercise any economic activity.
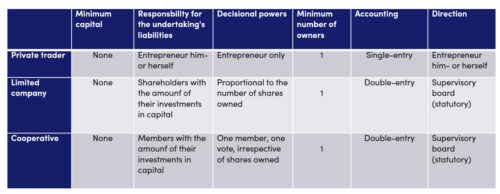
The next table compares cooperatives with limited companies and sole traders.
Different types of cooperatives
Cooperatives are well-suited for different sectors and various activities. They are usually classified according to their purpose or nature. Traditional, well-established cooperatives are generally called “producer cooperatives” (like cooperative dairies or slaughterhouses) or consumer cooperatives (like cooperative banks or shops).
Seen from the members’ relationship with the cooperative, it can work as a procurement cooperative or marketing cooperative, or it can be both simultaneously.
A procurement cooperative supplies to its members products, goods, or services they need in the household or their profession. Hence, a coop shop is a procurement cooperative. Typical purchasing cooperatives also include farmers’ purchase or machinery sharing cooperatives, merchants’ purchasing cooperatives, joint procurement cooperatives for food or consumer goods, and water and energy cooperatives. Procurement cooperatives can also contribute to collecting, processing, and marketing tasks.
A marketing cooperative takes care of marketing the products or services produced or provided by its members. The members are often entrepreneurs whose mutual cooperation allows them to take advantage of the cooperative under common marketing or a common label. A cooperative can market its entrepreneur members’ translation or hairdressing services, services for tourists, social, health, and well-being services, or cultural services.
An employ-owned cooperative is an undertaking belonging to its members, who have an employment relationship with it and who offer their work and know-how through it to external customers. This kind of cooperative can function in a single sector or specialize in some complementary sectors. It can be a multi-purpose company and offer temporary workforce also by non-members. This type of evolution started mainly in the 1990s when cooperatives became a more popular legal form for small enterprises. Sometimes this “new wave” of cooperatives has been called “new cooperative development,” as they were started in sectors traditionally absent from the cooperative field. These cooperatives function in numerous sectors, including information technology, construction, social and health services, energy production, water supply and sewerage, and marketing of different services or purchasing various equipment and machinery.
All cooperatives function under the same cooperative law. The Finnish Cooperative Act uses the term “closely held cooperative” for those with a maximum of 10 members.
SUMMARY:
Enterprise – together
A cooperative is a well-suited legal form for those who want to do business together. It pursues economic cooperation for the benefice of its members. It can be incorporated by one or more persons, companies, or corporate bodies, and it is well-suited for small and family businesses. A cooperative is a suitable means for any cooperation between entrepreneurs.
Capital
A cooperative allows for the combination of its incorporators’ know-how without significant initial capital. The capital is indefinite. The contribution for the share is determined in the statutory rules of the cooperative. The share is repaid if the member withdraws or if his or her membership is terminated. A cooperative has limited liability, and a member is only responsible for the cooperative’s obligations to the member’s contribution to the capital.
Decision-making
In a cooperative, the decision power is held by the members. In principle, the cooperative makes its decisions on the highest level by applying the principle of one member one vote based on democracy. During the general meeting, the members of the board of directors, which is a legally mandatory organ, are corporate bodies elected by the members. It is not compulsory to appoint a general manager.
Membership
The membership rules are flexible. The number of the members may increase or decrease during the functioning, where appropriate. In principle, a cooperative can admit or expel members, and a member can withdraw at any moment.
A flexible tool
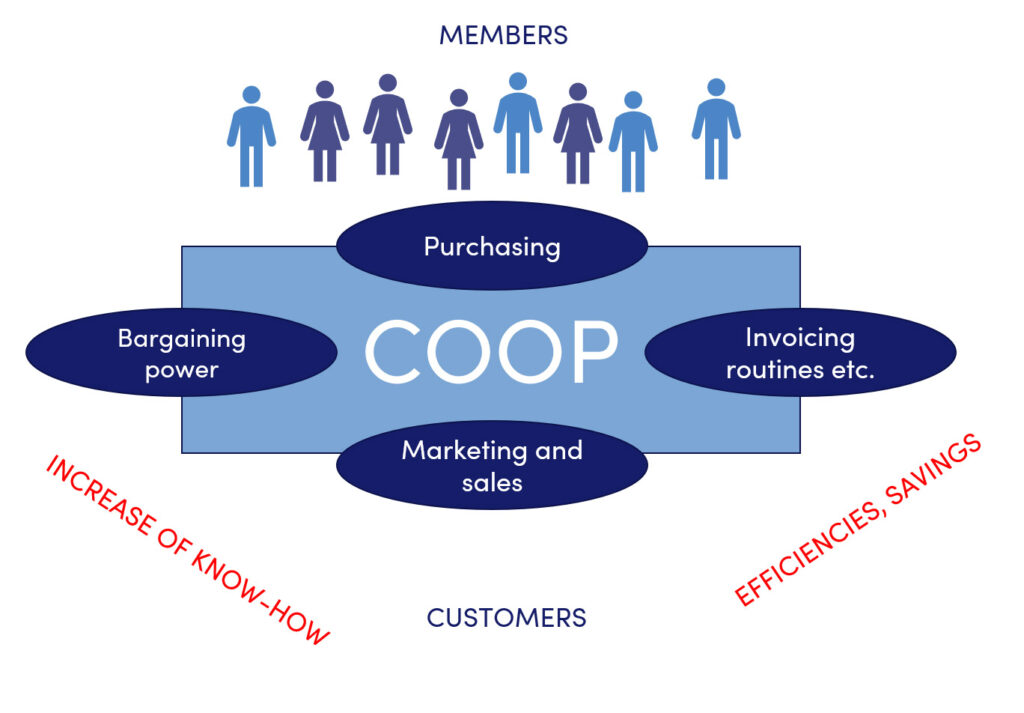
A cooperative can be assigned different tasks: procurement, marketing, sales, negotiation, and invoicing.